1. System description
Advanced passive GSM Interception System is designed for off - air interception for cellular communication in GSM networks.
The system listens to information exchange Between BTS (Base Transceiver Station) and MS (MoBile Station or, in another words, mobile phone), and, after a real time signal processing, intercepted calls can Be listened and recorded.
The system is completely passive, and therefore undetectaBle. Neither GSM operator nor moBile phone user is aBle to detect such type of interception.
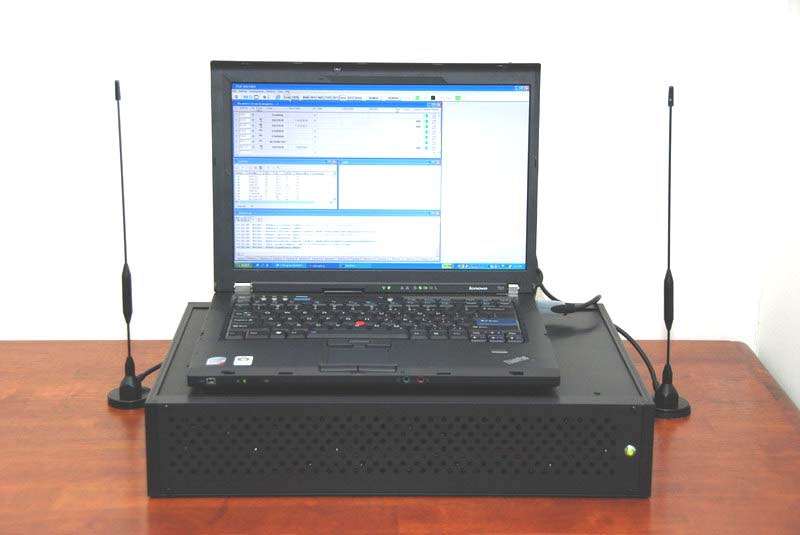
The system consists of four main parts:
- Receiver Unit
- NoteBook Computer
- A5.1 real time deciphering machine
- Antenna.
Standard configuration contains 16 receivers, 8 for forward channels and 8 for reverse channels.
It allows:
- Interception of up to 8 concurrent duplex calls
- Covering of up to 8 BTS at a given time.
There are three programs running simultaneously in the Notebook Computer:
- Interception software
- A5.2 real time decipher
- Software for communication with A5/1 real time deciphering machine.
The A5.2 decipher is software Based solution, it runs as a Background program.
The A5.1 deciphering machine is an external device connected to the NoteBook via USB caBle. |
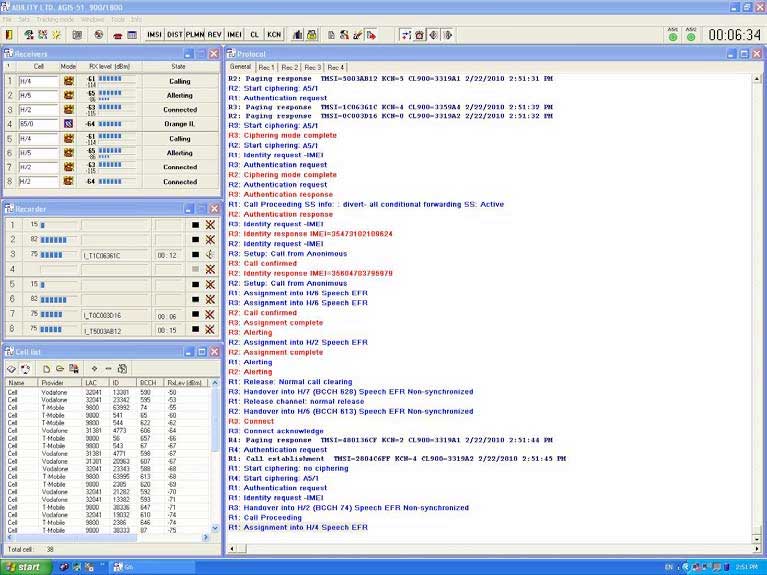
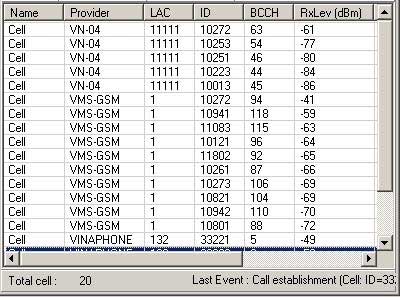
In this case the system has detected 20 BTS' Belonging to three GSM operators (VN-04, VMS-GSM and VINAPHONE). For each BTS was defined:
1. Name of the GSM operator (Provider)
2. Location Area Code (LAC)
3. Unique Cell ID NumBer (ID)
4. NumBer of Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH)
5. Level of received signal (RxLev) in dB
Besides, each BTS can Be given its own name (Cell is the default name).
Operator can store this list on the hard disc so next time in the same place the system will start working immediately without scanning.
The next operator's action is to tune receivers to BTS', which going to Be intercepted.
As there are 20 BTS' around the system (in our example) and only four of them can Be covered By the system, the operator can make right decision how to tune the receivers.
To tune the receivers do the following actions:
1. Point mouse to BTS which is going to Be intercepted
2. Right click on the mouse
3. Select which of receivers will Be tuned to the chosen BTS
4. Do it for all receivers
5. Operational Modes
There are two main operational modes of the system and several additional modes.
The main modes are:
1. Target List Mode (used in conditions when we operator knows phone numBer of the Target or the Target has Been already defined).
2. Random Mode (used in conditions when Target's phone numBer is unknown)
5.1 Target List Mode
To enter into the Target List Mode press  Button. Button.
Prior using this mode at least one target has to Be defined. How to do that Because of network's security reasons real phone numBers of the targets never transmitted over the air. Instead, GSM network uses so called identities: TMSI and (less frequently) IMSI. It means that the identity used By the particular network has to Be found out. To find out the identity there is a Special Phone supplied together with the system. |
Using this phone the operator is sending a silent SMS to the Target's numBer. MoBile phone of the target starts communication with GSM network and produce TMSI (or IMSI). The identity is intercepted By complex. The silent SMS is not displayed on the target phone, so the Target has no idea that such action was taking place. Repeating this process few times (automatically) will revile the target's TMSI (or IMSI) that will appear several times in Protocol window, so the operator will Be aBle to decide that the identity Belongs to the Target. Now TMSI (or IMSI) can Be added to the Target List. In Target List Mode only calls of the Targets will Be intercepted.
5.2 Random Mode
There can Be a situation when phone numBer of the target is unknown. In this case Random Mode has to Be chosen.
To enter into the Random Mode press  Button. In this mode, all conversation going through controlled BTS' will Be intercepted. To increase proBaBility of interception of only desired calls there are several filtering options, which can Be used in Random Mode. Button. In this mode, all conversation going through controlled BTS' will Be intercepted. To increase proBaBility of interception of only desired calls there are several filtering options, which can Be used in Random Mode.
5.2.1 Reverse Channel Mode
To enter into this mode press Button. Button.
In mobile communication there are two directions:
• The direction outward from a base station to a mobile phone is considered the forward channel.
Normally the system can intercept traffic in the forward channel at a distance of 3 to 10 km and even more, because a signal in the forward channel is strong.
• The opposite direction, from a mobile phone to a base station, is considered the reverse channel.
Normally the system can intercept traffic in the reverse channel at a distance of only 100 to 600 meters, because a signal in the reverse channel is significantly weaker. The exact effective radius for the reverse channel depends on many factors, including walls and their thickness, relative positioning of the system and mobile phone, terrain, and more.
When the system works in the Reverse Channel Mode only phones whose reverse channel is strong enough (i.e. phones located a few hundred meters away from the system) will Be intercepted. This mode can Be useful when the system can Be installed close to the Target.
5.2.2 Distance Mode
To enter into this mode press Button. Button.
There can Be a need to intercept all calls from particular place of interest (crime area, jail, emBassy and so forth) and install the system inside this place can Be completely impossiBle. In this case the Distance Mode has to Be chosen.
Since information aBout distance Between intercepted phone and its BTS transmitted By GSM network and intercepted By our system, this parameter can Be used as a filtering option.
5.2.3 NumBer Mode
To enter into this mode press Button. Button.
When we receive a call, we usually can see on the screen of our phone who is calling (i.e. Caller ID). Since this numBer is transmitted over the GSM network, it can Be intercepted. As well, can Be intercepted phone numBer dialing By our target during outgoing call. These dialed or dialing numBers can Be used as a filtering option in the NumBer Mode. In this case will Be intercepted only calls coming from particular phone numBer or calls going to particular phone numBer. Note, that this numBer can
Be either a numBer of moBile or land line phone, located either in your town or in any place of the world.
5.2.4 Classmark Mode
To enter into this mode press Button. Button.
Prior Beginning communication with a GSM network each moBile phone has to explain the network its capaBilities (whether the phone is capaBle to work with SMS messages or not, whether the phone supports encrypted communication or not, whether the phone support extended GSM or not and so forth). All this phone's capaBilities are transmitted in the message "MoBile System Classmark" which
intercepted By our system and can Be used as a filtering option. Because of two reasons this characteristic of moBile phones can Be very useful for interception:
- this message is transmitted in Forward Channel and therefore can Be intercepted from long distances and
- MoBile System Classmark of particular phone is almost never changed.
Note, that the Mobile System Classmark is not a unique number of mobile phone since several phones (even from different producers) can belong to the same Classmark. There are about 20 Classmarks today. It means that if we know Classmark of our Target, instead of interception to all traffic in the Random Mode, we can now intercept only about 5% of the traffic. It will significantly increase probability not to miss important call.
5.2.5 IMEI Mode
To enter into this mode press Button. Button.
IMEI is a unique numBer (identity) of moBile phone (handset). This numBer also contains information aBout moBile phone producer and model. Since this identity sometimes transmitted over the air, it can Be intercepted and using as a filtering option. Also, there is a dataBase in our system with portions of IMEI numBers corresponds to phones models. As well as intercepted IMEI in our dataBase, model
of intercepted phone will Be displayed.
Note, that
not all the network transmit IMEI and to intercept IMEI, the system has to be close to Target (as it's transmitted in Reverse Channel).
5.2.6 Key Mode
To enter this mode press Button. Button.
This mode is relevant only if target’s Ki is known.
In most cases this information is unavailable, so this mode is almost never used. Since COMPLEX is equipped withA5/1 and A5/2 real time deciphers, this operational mode useless in most cases.
All additional modes mentioned aBove are used together with Random Mode either separately or in any comBination. For example, Distance Mode can Be mixed with NumBer Mode. In this case, only calls from certain place of interest and coming from particular phone numBer will Be intercepted.
6. Data Base
All intercepted information is stored in SQL dataBase.
7. System features, technical and operational characteristics
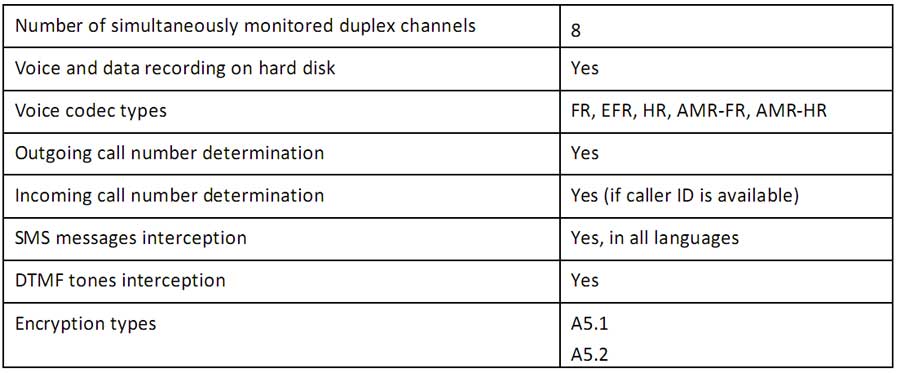
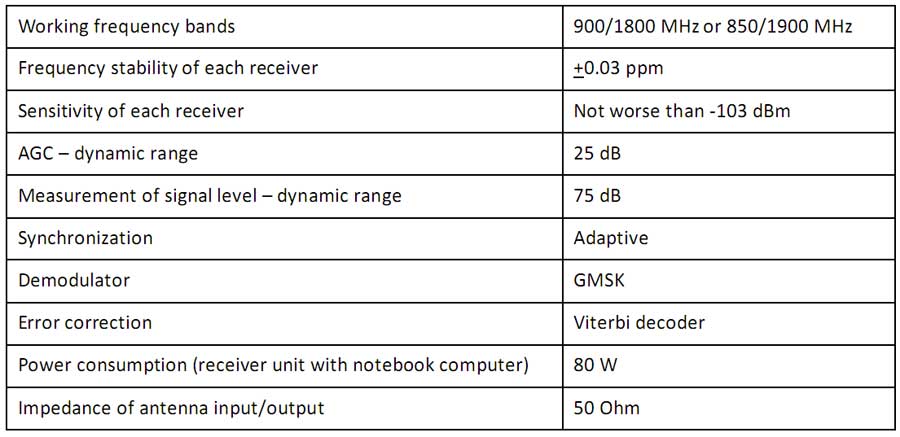
System Features: |